冯康请我吃北京鸭时,遇见了陈景润
冯康请我吃北京烤鸭时,遇见了陈景润 1972年,李建华教授和我在中国最早研发了三维有限元方法和应用,1973年 … 继续阅读
https://weibo.com/tv/show/1034:4405060357276488
Ganquan Xie1,2, Jianhua Li1,2 (Corresponding Author, glquan18@qq.com),
Feng Xie2, Lee Xie2
1 GL Geophysical Laboratory, USA
2 Dayuling Super Science Computational Center,
Wang Chen, Changsha, Hunan, China.
Abstract
https://weibo.com/tv/show/1034:4405060357276488
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/draft/preview/7416672848762589184
GLLH 电磁隐形斗篷采用新型双前向分支结构,能够吸收并重塑波前,没有无限速度,没有超光速,也没有时间延迟。GLLH 电磁隐形斗篷是世界上首款完全隐形的斗篷。该论文的预印本已于2010年5月24日在 arXiv.org/abs/1005.3999 上发布,是世界上最早的不超光速的完全隐形披风。此版本仅为改善的英文校对版本。这是最重要和最早可实现的隐形披风。希望同志们高兴。
基于GLLH隐形斗篷,我们发现了正空间和负空间以及隐形科学;各向同性电磁隐形GLHUA球体;各向异性电磁隐形GLHUA斗篷。
三维负空间是三维正空间的对应空间。我们-老中青少幼胎的我们-和动物清醒时,我们在正空间中千奇百怪扶风唤雨地活动;当我们睡着时,我们百怪千奇唤雨扶风美梦负空间。
陈景润是伟大的数学家,我们把陈景润证明中的形式引为无散射反算的搜索材料类,发现和反明了世界上笫一个和唯一个不超光速的完全隐形批风,進而突破和发现了正空间和负空间。获得了一个在正空间的科学在负空间也成立的理论。突破了筛法,分辨出1十1和1十2。在陈景润定理基礎上,运用负空间理论可以证明哥德巴赫猜想。美籍华人超级科学家任峻瑞教授,Professor Erica Jen , 给了我们无私和巨大的帮助。我们的陈景润哥德巴赫猜想证明的进展论文会包函任峻瑞和许连科的名字。
GLLH EM invisible cloak with novel two front branching, absorbing and creating wave front, without infinite speed and without superluminal and without time delay. GLLH EM invisible cloak is completely invisibility cloak first in the would. The preprint of this paper has been announced in arXiv.org/abs/1005.3999 on May 24, 2010, first in the world This version is just proofread in English.
We propose new Global and Local (GL) electromagnetic (EM) cloaks with a distinctive class of materials
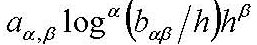
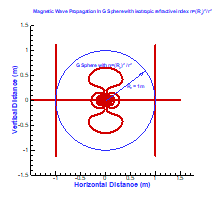
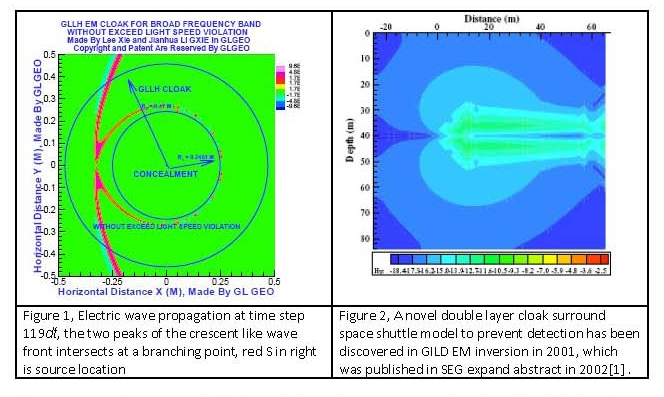
(GLLH cloak) without superluminal propagation. The refractive index of the GLLH cloak material, is greater than one or equal to one. Our GLLH cloak is created by GL EM modeling and GL EM cloak inversion with searching class, *. The GLLH cloaks in this paper have finite speed, exhibit no superluminal physical violations, and offer additional advantages. The GLLH EM cloaks can be practical using normal materials and are applicable over a broad frequency band. The GL EM cloak inversion and electromagnetic integral equation for the cloak are presented in this paper. The novel EM wave propagation and front branching in the GLLH cloak by GL EM modeling are also presented. At time step 118 dt, in the GLLH cloak, the wave front is curved like a crescent. At time step 119 dt, its two crescent front peaks intersect at a front branching point, where the front splits into two. The novel front branching and crescent- like wave propagation are displayed in the Figure 1, Figure 2, and figures 5 -20 in this paper. From the GLLH invisible cloak, we discovered positive space and negative space and invisible science; isotropic electromagnetic invisible GLHUA sphere; anisotropic electromagnetic invisible GLHUA cloak.
All copyright and patent rights of the GLLH EM cloaks, GL modeling and inversion methods are reserved by the authors in GL Geophysical Laboratory.
The corresponding author Jianhua Li submitted this paper to peer review, and also announced it as a preprint only on SSRN.
Author Contribution Declaration: Corresponding author Jianhua Li is the research leader of this paper and our invisibility science, ideas, concepts, formulas, and overall organization and arrangement. Professor Feng Xie, Lee Xie, and Ganquan Xie contributed to the ideas, concepts and formulas of this paper. Feng Xie wrote the software; Lee Xie made the figures and videos.
Funding declaration: There is no funding to support our paper “GLLH EM Invisible Cloak With Novel Front Branching And Without Exceed Light Speed Violation”. We have disabilities and volunteered for invisibility science for 25 years, never applying any funding to support our research “Electromagnetic invisible GLLH cloak” and “Electromagnetic invisible GLLH Sphere” and no funding for our “invisible science” research.
The data availability statement:
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
All invisible GLLH cloak analyzed during this study are included in this published article by
corresponding author Jianhua Li and co authors. In this paper and our study, corresponding author Jianhua Li and all co authors did not use any external data. All of the material and contents in this paper is owned by the authors in this paper. Fortran programs for the simulations in this paper were written by us.
I. Introduction
In this paper, we propose new Global and Local (GL) electromagnetic (EM) cloaks with a distinctive class of materials (GLLH cloak) without infinite speed violation, without superluminal propagation, and without time delay. The refractive index of the GLLH cloak material, is greater than one or equal to one. Our GLLH cloak is created by GL EM modeling and GL EM cloak inversion with searching class, *. We name our cloak as GLLH cloak. The GLLH EM cloaks can be practicable by using normal materials and are available for all broad frequency band.
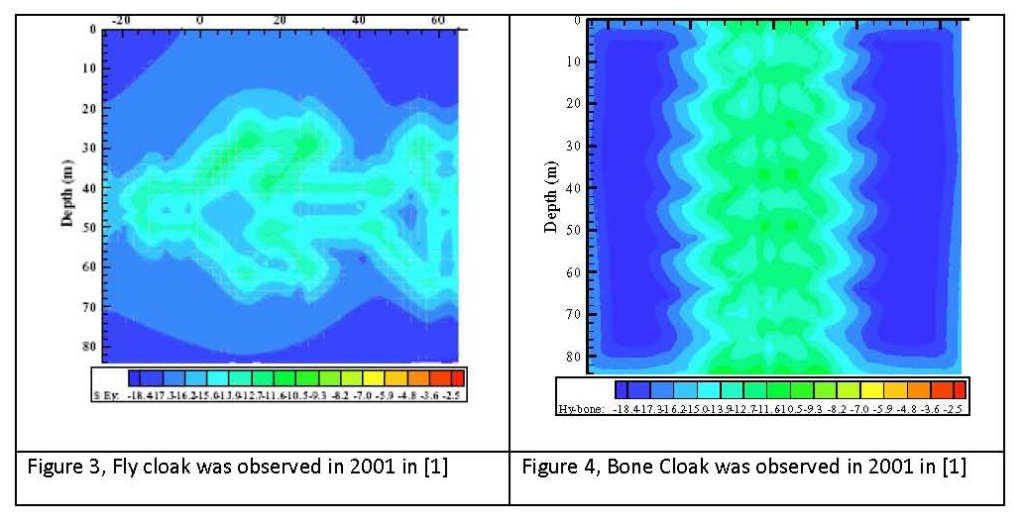
In 2001, we used Global Integral and Local Differential (GILD) EM modeling and inversion to detect the fly model imaging from EM sources in some frequency band. A strange cloak phenomenon was discovered in the residual field. The cloak protects the fly object from the exterior EM field detection. We called the strange phenomena as GILD effect and published it in paper [1]. In this paper, We present the discovered cloaks imaging again in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
To investigate the strange double layer clothes phenomenon , we developed the Global and Local field electromagnetic modeling method [ 2 ] and GL Metro Carlo inversion method [ 3 ]. These new methods are completely different from the traditional finite difference scheme [ 4 ] and finite element method [ 5 ]. The GL method has total advantages over the traditional methods. Large matrix solving costs and error reflections on artificial boundaries are difficulties in traditional numerical simulation methods. The GILD EM modeling and inversion [ 6 ] represent important progress in overcoming these difficulties. The GL EM modeling and GL Metro Carlo inversion have advantages in completely overcoming these historical difficulties [ 2 , 3 ]. In physical and quantum mechanical simulations, the Born approximation [ 7 ] is often used. However, Born approximation is inaccurate and cannot be used in high frequency bands or with high contrast and singular materials. We used GL EM modeling and inversion to simulate the double layer clothes phenomenon [ 1 ], discover a mirage image [ 8 ], and propose the GL double layer cloak [ 9 – 13 ]. Pendry et al. proposed the single layer cloak using transformation optics in [ 14 ] (Pendry cloak ). However, exceeding light speed and infinite EM wave field speed are its two main physical violations. In [ 15 ], we proved a theorem that no Maxwell wavefield can be excited by sources inside the single layer cloaked concealment, if the cloak material parameters are Pendry cloak , and the concealment is filled with basic EM materials and . By this theorem, no EM wave can be excited in the Pendry cloak cloaked concealment, which is its third physical violation. Our GL double layer cloak [ 9 – 13 ] overcomes this difficulty. The GL outer layer cloak provides invisibility functions. The GL inner layer cloak decays the internal wavefield so that it cannot propagate outside the inner layer. There is no exceeding light speed violation in the GL inner layer cloak. However, the Pendry cloak is strongly degenerate material, in which [ 14 ] the n(r) less than one , when x = Ri, n(R1)=0 , it is evidence that Pendry cloak has infinite speed violation. When Ri < r < Ro, Pendry cloak has superluminal propagation fundamental problem. We proposed a GLWF double layer EM cloak in a broad frequency band [ 16 ] to overcome exceeding light speed. Figure 9 in [ 16 ] shows that EM wave propagation in the Pendry cloak exceeds ligh speed. Figure 7 in [ 16 ] exhibits that EM wave propagation in the GLWF double layer cloak does not exceed light speed. As a great advance over the GLWF cloak [ 16 ], by using GL Metro Carlo non scattering inversion [ 3 ], we propose new GLLH cloaks with class material *, one of which is formulated by ( 2)- (5 ) in this paper. The GLLH invisible cloak has nonzero and positive ,n(r) > 1, and in the whole cloak domain, which is its large advantage over the second order strongly singular Pendry cloak with zero relative refractive index parameters on the inner boundary , which is instant evidence that the Pendry cloak exhibit an infinite speed violation and has a fundamental superluminal propagation problem. We proved that the relative refractive index of our GLLH cloak is larger than or equal to one, n(r) > 1, in the whole cloak domain , when Ri=0.2491 m, Ro=0.47 m.
By using GL EM modeling [ 2 ], the novel full EM wave propagation in the cloak shows that there is no exceeding light speed violation in our GLLH cloak in this paper.The novel EM wave propagation and distinct front branching in the GLLH cloak by GL EM modeling are presented in this paper. Figures 8-13 show that the wave front is successively curved like a crescent and propagates slower than light in free space. In particular, at time step 118 dt in the GLLH cloak, Figure 1 shows the curved EM wave front is very similar to a crescent. At time step 119 dt, the electric wave inside the GLLH cloak propagates slower than light speed; moreover, its two crescent peaks intersect at a novel front branching point. At the front branching point, the front splits into two fronts. One is the outgoing front, which propagates forward out of the cloak and carries most of the wave energy. After the outgoing front propagates out of the GLLH cloak, it recovers to the original wave front in free space. The other front is similar to a spherical surface wave and propagates attractively toward the inner boundary. The attractive front propagation is very slow. Its amplitude and speed rapidly decay to zero. The attractive front propagates toward the inner boundary, but cannot reach to it at r= Ri. The novel front branching and crescent- like wave propagation are displayed in Figures 1,2,and 5-20 in this paper. When the source is located outside the GLLH cloak and the observation point, (r,θ,φ) is inside the cloak approaching the inner boundary , r=Ri, the EM wave field decays to zero in the inverse radial direction. On the inner boundary, the radial electric wave field , E going to zero , and the radial magnetic wave field, H going to zero, absorbed, simultaneous outgoing wave is creating, which is a distinctive property of the GLLH invisible cloak. Ulf Leonhardt et al. proposed a new cloak with finite speed based on a Euclidean and non- Euclidean joint transform [ 17 ]. The ULF cloak overcomes the ” infinite speed ” physical violation, even though its refractive index is less than one in some subdomains. Chen et al and Zhang et al proposed an analysis for Pendry cloak using Mie transform [ 24 ][ 25 ]. The creation motivation of our GLLH cloak is according to our double layer cloth observation in 2001, which is shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, and our 3D FEM super convergence observation in 1973 [ 5 ][ 18 ][ 19 ]. The form
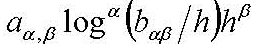
(*)
is used as an estimation form in number theory [ 20 ][ 21 ][ 22 ], PDE, numerical mathematics [ 5 ][ 23 ], probability, geometry, and in other estimation theory in physics and other sciences. However, no one thought it could be used in invisible cloak material before this paper. Fortunately, the form * is used as the search class of the GL cloak non scattering inversion to create the GLLH invisible cloak, which is our inspiration and discovery. The finding inversion is to find the object from the observer-measured scattering wave from the object excited by control or natural sources. The invisible cloak generation is hiding inversion. The invisible and hiding inversion is to generate a cloak material such that the scattering wave from the cloak is zero. The double-layer cloth and fly imager in Figure 3 and Figure 4 show that the finding inversion and hiding inversion contradict and compromise each other. From the GLLH invisible cloak, we discovered positive space and negative space and invisible science; isotropic electromagnetic invisible GLHUA sphere; anisotropic electromagnetic invisible GLHUA cloak. What is the positive space and negative space? Just as before, without imaginary number, i=√(-1) , we cannot solve the equation x²+1=0 in the real number domain. Let’s ask: In polar coordinates on a two-dimensional plane, where ,(ρ,θ), ρ>0 , is a point on the plane, where is (-ρ,θ) for the same value θ? This question can intrigue students from elementary middle school to university, and has also attracted the attention of professors and scientists at all levels. In this article, we introduce the concepts of positive space and negative space. In the three-dimensional spherical coordinate system, the set of points with positive radial coordinates,(r,θ,φ), 0≤r≤+∞, is called three-dimensional positive space. This is the three-dimensional space we live in. In the three-dimensional spherical coordinate system, a point with negative radial coordinates,(-r,θ,φ) ,-∞≤-r≤-0 , is defined as three-dimensional negative space, as described in our paper [15][16]. The origin of the positive space can be anywhere. The point in the positive space,(r,θ,φ) , and the point in the negative space,(-r,θ,φ) , are corresponding points with the same longitude and latitude. The origin of the positive space, +0, and the origin of the negative space, -0, are corresponding points, but different points. The three-dimensional negative space is the corresponding space of the three-dimensional positive space. When we are awake, we act in all kinds of strange ways in the positive space; when we are asleep, our sweet dreams are in the negative space.
The structure of this paper is as follows: The introduction is in Section 1. In Section 2, we propose a new GLLH EM cloak without exceeding the speed of light. The GL EM cloak inversion is proposed in Section 3. In Section 4, we present novel wavefront branching and EM wave propagation in the GLLH cloak without exceeding the speed of light. The distinct invisibility properties of the GLLH EM cloak are discussed in Section 5. In Section 6, we propose a GLLH EM double -layer cloak. In Section 7, we show that the EM wave field decays to zero inversely with radius. Section 8 describes an advanced GLLH Invisibility AGLLH Cloak . Section 9 describes the history and discussion. The conclusion is in Section 10 .
II. GLLH EM CLOAK WITHOUT EXCEEDING LIGHT SPEED
In this section, we propose a new GLLH EM invisible cloak for a broad frequency band
without exceeding the light speed violation
A GLLH EM INVISIBLE CLOAK
In the Maxwell equations

Where E is the electric wave vector field, H is the magnetic wave vector field ,

We propose the GLLH EM invisible cloak material parameters in a 3D spherical coordinate system. The cloak material parameters are radial dependent as follows:


Where Ri < r < Ro is the spherical annular cloak domain, Ri is the inner radius of the annular cloak, Ro is the outer radius of the annular cloak, ε is the dielectric parameter matrix, μ is the permeability parameter matrix, ε₀ is the base dielectric constant , μ₀ is the base magnetic permeability constant, ε_r is the relative radial dielectric permittivity, μ_r and are the relative angular dielectric permittivity, εr is the radial relative permeability, and are relative angular permeability.
- INVISIBLE FUNCTIONS OF GLLH EM CLOAK
Function I:
When the source and observer are located outside the cloak, we verified the invisible function I of the GLLH EM cloak materials in (4)-(5) as follows:
Non scattering from the cloak to disturb the exterior EM field,

Function II
When the source is located outside the cloak and observer is inside the cloak, we verified the invisible function II of the GLLH EM cloak materials in ( 4 )-( 5 ) as follows:
Exterior EM field does not penetrate into the concealment region:

Our GLLH EM cloak completely overcomes the “exceed light speed” and “infinite speed” two physical violations in the Pendry cloak. The GLLH EM cloak as GL outer layer cloak and the GL inner layer cloak ( 3 )-( 5 ) can be coupled to construct new GLLH EM double layer cloak.
III GL EM CLOAK INVERSION
We propose a GL EM inversion for cloak in this section. Ii is based on the 3D EM integral equation and GL EM modeling in [ 2 ] and the GL Metro Carlo inversion in [ 3 ].
- 3D EM INTEGRAL EQUATION


where E is the electric field intensity, H is the magnetic field intensity, r ,is the observation space location variable, rs is the source space location variable, t is time, Eb is the background electric field intensity , Hb is the background magnetic field intensity, ,G is the 6 × 6 EM Green’s tensor matrix, Gb, is the background 6 × 6 EM Green’s tensor matrix, diag[] is the 6 × 6 variation EM material matrix as follows:

Where , ε is the relative permittivity parameter matrix, μ is the permeability parameter matrix, the relative permittivity and permeability can characterize isotropic or anisotropic materials, ε₀ is the base permittivity constant , μ₀ is the base magnetic permeability constant, εr is the relative radial dielectric permittivity, ε_θ and ε_φ are the relative angular permittivity . μr is the radial relative permeability, μ_θ and μ_φ and are relative angular permeability. For the GLLH cloak material, the ε and μ are proposed in formulas (2) − (5) in this paper.
B. FUNCTIONS IN GL EM CLOAK INVERSION
We propose a GL EM cloak inversion for an GLLH invisible cloak in this section. Two invisibility functions are required for the GLLH EM cloak without exceeding light speed: ( I ) the exterior EM field should not be scattered or should not be interfered by the cloak; ( II ) the exterior EM field cannot penetrate into the concealed region of the cloak; and ( III ) no exceeding of light speed.
C. GL EM CLOAK EXTERIOR INVERSION
When the source and observer are located outside the cloak , we present the cloak invisibility function I via the following inversion.
The exterior EM field must not be disturbed by scattering from the cloak.
According to the invisibility function I ( 6 ) and using the EM integral equation ( 8 ), we have

and using the EM integral equation (9), we have

D. GL EM CLOAK INNER INVERSION
When the source is located outside the cloak and observer is inside the cloak, we present the cloak invisibility function II via the following inversion.
The exterior EM field cannot penetrate into the concealed region of the cloak
According to the invisibility function II ( 7 ) and using the EM integral equation ( 8 ), we have

and using the EM integral equation (9), we have

E. CONSTRAINT IN GLLH EM CLOAK INVERSION
We present the without exceeding light speed violation as the constraint of the GLLH EM cloak
inversion, for the radially dependent and ,

F. GL EM CLOAK INVERSION
The EM integral equations ( 11 ) and ( 12 ) for and , the EM integral equations ( 13 ) and ( 14 ) for , and , and the “no exceed light speed ” radially dependent constraint ( 15 ) are coupled to construct the GL EM cloak inversion for the EM invisible GLLH cloak. We use the GL EM Metro Carlo inversion method in [ 3 ] to solve the GLLH EM cloak inversion, and find the radial – dependent GLLH EM cloak material that satisfies the GL EM cloak exterior inversion ( 11 ) and ( 12 ), the GL EM cloak inner inversion ( 13 ) and ( 14 ), and constraint ( 15 ) without exceeding light speed violation.
IV. NOVEL EM PROPAGATION IN GLLH EM CLOAK WITHOUT EXCEEDING LIGHT SPEED
In this section, we present a novel EM propagation in the GLLH EM cloak without exceeding light speed. The EM wave propagation pattern is completely new, and has never been shown in other authors’ papers.
A. THE SIMULATION MODEL OF THE GLLH EM CLOAK
The simulation model: the 3D domain is [− 0.5 m , 0.5 m ] × [− 0.5 m , 0.5 m] × [− 0.5 m, 0.5 m ], the mesh number is 201 × 201 × 201, the mesh size is 0.005 m. The electric current point source is defined as

where the denotes the location of the point source, the unit vector is the polarization direction, the time step dt=0.3333 x 10-10 Second, the frequency band is from 0. 05 GHz to 15 GHz, the highest frequency f =15 GHz, and the shortest wavelength is 0.02 m. The GLLH EM cloak consists of the spherical annulus centered at the origin and is filled with GLLH EM cloak materials, where meter, meter. The cloak is divided into 90 × 180 × 90 cells. Spherical coordinates are used in the region , while Cartesian coordinates are used in outside the sphere to mesh the domain. In the following, ,.
B. NOVEL ELECTRIC WAVE PROPAGATION
The electric intensity wave is excited by the point source S, denoted by a red S in the figures in this paper. In Figures 1 – 2 and Figures 5 – 18, the source ( red S ) is located in free space, on the right side outside of the entire GLLH EM cloak, at ( 0.83 m , 0. 0, 0. 0 ). In Figure 19, the point source ( red S ) is located on the left outer side of the point source marked by the red S is located on the left outer side of the cloak, at (− 0.83 m, 0. 0, 0. 0 ). In Figure 20, it is located on the bottom outer side the cloak, at ( 0. 0, −0.83m , 0. 0 ). In Figure 5, at time step 40 dt, the electric wave, Ex, inside the GLLH EM cloak, R1 ≤ r ≤ R2, propagates no faster than the speed of light. Figure 6 shows that at time step 50 dt, the electric wave, Ex, inside the GLLH EM cloak , R1 ≤ r ≤ R2, propagates no faster than the speed of light. In Figure 7, at time step 60 dt , the electric wave, Ex, inside the GLLH EM cloak R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 propagates slower than the speed of light. Figure 8 shows that at time step 70 dt, the electric wave, Ex, inside the GLLH EM cloak R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 propagates slower than the speed of light. n Figure 9, at time step 80 dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 propagates slower than the speed of light. Figure 10 shows that at time step 90 dt, the electric wave, Ex, inside the GLLH EM cloak, R1 ≤ r ≤ R2, propagates slower than the speed of light. In Figure 11, at time step 100dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2) propagates slower than light speed. Figure 12 shows that at time step 110dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) propagates slower than light speed. In Figures 1 and 13, at time step 119 dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) propagates slower than light speed. Figures 2 and 14 show that at time step 120dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) propagates slower than light speed. The upper and lower parts of the curved electric wave front intersect at a branching point. These branching points form a 2D surface that depends on the source location. In these figures, the red S denotes the source, located to the right of the cloak. The front branching point is located to the left of the concealment. In Figure 15, at time step 121dt, the electric wave , Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2) propagates slower than light speed. At time step 121dt, the wave front inside the GLEM cloak is split into two fronts at the branching point. One wave front continues propagating outward, slower than the light speed. The other closed wave front propagates inward toward the inner boundary r = R1 of the cloak, much slower than the light speed. The speed of the inward wave front approaches zero, and its amplitude rapidly decays to zero. In Figure 16, at time step 122 dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak (R1 ≤ r ≤ R2) propagates slower than light speed. The other inward wave front propagates much slower than the light speed, with its speed approaching zero and its amplitude rapidly decaying to zero. In Figure 17, at time step 130dt,the electric wave, x inside the GLEM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) propagates slower than light speed. The other inward wave front propagates much slower than the light speed, with its speed approaching zero. In Figure 18, at time step 133dt, the outgoing front of the electric wave, x propagates out of the GLEM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) and recovers to wave in a free-space wave, and is not scatter – interfered by the cloak . The other inward wave front propagates much slower than the light speed. It propagates toward the inner boundary r = R1 of the cloak , with its speed approaching zero.
In Figures 1, 2, and 5– 18, the source is denoted by the red S, located to the right of the cloak. Figure 19 shows that at time step 120dt, the electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) propagates slower than light speed. The upper and lower parts of the curved electric wave fronts intersect at a branching point on the right. These branching points form a 2D subsurface depending on the source location. In this figure, the red S denotes the source, located to the left of the cloak. The front branching point is located to the right of the concealment. In Figure 20, at time step 120dt, the electric wave , Ex inside the GLEM cloak ( R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 ) propagates slower than light speed. The left and right parts of the curved electric wave fronts intersect at a branching point on the top side . These branching points form a 2D subsurface depending on the source location. In this figure, the red S denotes the source, located at the bottom of the cloak. The front branching point is located on the top side of the concealment.
V. INVISIBLE PROPERTIES OF GLLH EM CLOAK
By using the GL EM Metro Carlo inversion method in [ 3 ], we solve the GL EM cloak inversion ( 11)-(15) and obtain the GLLH EM invisible cloak. The invisibility properties of the GLLH EM cloak are verified in this section.
A. The Invisibility of the GLLH EM Cloak
Statement 1: The exterior EM field is not scattering – interfered by the cloak.
Because of our GLLH EM exterior cloak inversion,— by substituting the GLLH EM cloak parameters in ( 2)–( 5 ) and the EM wave field by GL modeling [ 2 ] into ( 11 ) and ( 12 ), such that integral equations ( 11 ) and ( 12 ) hold —we have identity ( 6 ): no reflection and no scattering from the cloak to interfere with the exterior EM field in free space.
By calculations, when Ri = 0. 2491 meter and Ro = 0. 47 meter, we prove that on the outer boundary of the cloak , and in (2) – (5) satisfy the condition for any exterior source and frequency. Therefore, any exterior EM wave field must not be scattering -interfered by the cloak. By the 3D GL EM modeling [ 2 ] simulations, electric wave propagations in Figures 5–18 verify that there is There is no reflection and no scattering from the cloak to interfere with the exterior EM field in free space.
By calculations, when Ri=R1 = 0. 2491m and Ro =R2= 0. 47m, we can prove that on the outer boundary of the cloak at r = Ro=R2, relative and in ( 2)–( 5 ) satisfy

This is a necessary condition for the invisibility of the cloak. From the GLLH EM cloak exterior inversion equations ( 11 ) and ( 12 ), we can prove that condition ( 17 ) is necessary.
Statement 2: Any exterior EM wave field cannot penetrate into the concealed region. From the GLLH EM inner cloak inversion equations ( 13 ) and ( 14 ), and EM integral equations ( 8 ) and ( 9 ), Statement 2 is proved. Also, because on the inner boundary r = Ri=R1, the relative refractive index or in (4)–(5 ) is infinite, from the convergence of integrals (11)–(14 ),requires that the EM wave field must vanish
on the inner boundary r = Ri=R1. We obtain the conditions

Conversely, the conditions ( 17 ) and ( 18 ) are sufficient for the invisibility of the GLLH EM cloak.
B. Without Exceeding Light Speed Violation
Statement 3: The relative refractive index in the GLLH EM cloak configuration in this paper is larger than one, and the group speed in the cloak is finite and less than c ( in units where c = 1 ).
From ( 4 ), theand are finite , positive , and monotonically increasing functions of r in the Ri =R1≤ r ≤ Ro=R2. Moreover, their minimum value on the inner boundary of the cloak are

their maximum value on the outer boundary ; at Ro = 0. 47 mof the cloak, both are one. From( 5 ), and are monotonically decreasing functions of r in the R1= Ri ≤ r ≤ Ro =R2. Moreover, their maximum value on the inner boundary of the cloak is infinite, and their minimum value on the outer boundary, Ro = 0. 47m is one.
The relative refractive index of the GLLH EM cloak in ( 2 )-( 5 ) is

The group speed is finite and .Therefore, in the annular region R1 = Ri ≤ r ≤ Ro =R2, with Ri = 0. 24 m and Ro = 0. 47 m, the GLLH EM invisible cloak material in ( 2 )-( 5 ) has no violation of exceeding light speed. The novel electric intensity wave propagations, shown in Figures 5 – 18 in ( 2 )-( 4 ) that verify the GLLH EM cloak is an invisible cloak without exceeding light speed violation.
C. Wave Front Branching
The EM wave propagation in the GLLH EM cloak is completely novel, as displayed in Figures 1 and 2 and in Figures 10 to 19. In particular, in Figure 14, the EM wave front is curved around the concealment, and its upside and downside parts intersect at a movable branching point, forming a 2D subsurface. Figure 15 shows that the two wave fronts propagate separately from the branching point. The first wave front is forward propagating outgoing. The second wave front is attractively propagating and approaching to the inner boundary r = Ri. The speeds of both wave front propagations slower than the light speed. The second wave front’ s attractive propagation is very slow. Its amplitude rapidly decays to zero. Its propagation speed approaches zero. The front branching points form a movable 2D subsurface that depends on the source location. The front branching point and source are separately located on opposite sides of the concealment region. In Figures 14 and 15, the source ( denoted by red S ) is on the right side of the cloak, while the front branching point is on the left side of the concealment. In Figure 19, the source ( red S ) is on the left side of the cloak, and the front branching point is on the right side of the concealment.
In Figure 20, the source (red S) is located at bottom of the cloak, and the front branching point is located in at the top side of the concealment. These novel EM wave propagations in the GLLH EM cloak and the wavefront branching phenomenon are displayed only in this paper. They do not appear in other cloak papers. The GLLH EM cloak, novel wave propagations, and wavefront branching are patented and copyrighted by the authors at GL Geophysical Laboratory.
VI. GLLH EM DOUBLE – LAYER CLOAK
We propose a new GLLH EM double – layer cloak in this section.
Statement 4: The concealment region of the Pendry cloak, with the basic EM materials ε₀ and μ₀, if incident is modified electromagnetic wave, then no EM field can be excited by a source inside the concealment region.
VII. EM WAVE FIELD DECAY TO ZERO INVERSE RADIAL
Statement 5 : The concealment region of the GLLH invisible cloak, with the basic EM materials ε₀ and μ₀ or normal material with refractive index n ≥ 1, then no external incident wave can not penetrate the concealment.
We have proved the statement 4in [ 10 ] and [ 15]. Statement 5 theoretically confirms that our double – layer cloak phenomenon in 2001 in [ 1 ] is a credible physical discovery . We proposed the GL double – layer cloak in [ 9 ], [11],[ 12], [ 13 ], and [ 16 ], and a new GLLH EM double – layer cloak here without superluminal violation. The inner layer cloak of the GLLH EM double – layer cloak is the same as in ( 1 ) of [ 11 ] or ( 1 ) of [ 9 ], [ 12 ],[ 13 ], and [ 16 ]. The GLLH EM cloak is used as the GL outer layer cloak of the new GLLH EM double – layer cloak. In the GL inner cloak, an EM wave can be excited by a source inside the concealment , rapidly decays when the EM wave propagating into the GL inner layer, slowing far below light speed and approaching zero at the outer boundary of the inner cloak. There is no any reflection back to the concealment from the GL inner layer cloak, and the EM environment inside the concealment is remains normal. The GL outer layer cloak provides full invisible functions for invisibility over a broad frequency band, has a refractive index large greater than one, and involves no superluminal violation. The reciprocity law is satisfied. Therefore, our GLLH EM double – layer cloak overcomes the three physical violations present in the Pendry cloak or in other follow Pendry cloaks. The Pendey cloak is a single – layer cloak with infinity speed violation and superluminal fundamental problem. By Statement 4 , no EM wave can be excited by a source inside the concealment of the Pendry cloak, causing its third physical violation.
Statement 6 : When the source is located outside the GLLH invisible cloak in ( 2 )-(5 ), the observer at r is inside the cloak and approaches the inner boundary r = Ri, the EM wave fields decay to zero in the inverse radial direction. We have
Er ( r, θ, φ) = E θ( r, θ, φ) = E φ = 0, at r = Ri,
Hr ( r, θ, φ) = H θ( r, θ, φ) = H φ = 0, at r = Ri, ( 21 )
where r = Ri is the inner boundary of the GLLH cloak. On this inner boundary r = Ri, the radial electric wave field Er ( r, θ, φ) = 0 and the radial magnetic wave field Hr ( r, θ, φ) = 0 are distinctive properties of the GLLH invisible cloak. On the inner boundary of other transformed cloaks , the radial wave EM fields are not zero.
VIII. Advanced GLLH Invisibility AGLLH Cloak
From

We find an original function

The topological transformation (22) maps the spherical annular region, in the positive space one to one onto the exterior of the negative sphere in the negative space, which induces an advanced anisotropic electromagnetic invisibility AGLLH cloak. The radial magnetic wave propagation through the AGLLH cloak and GLLH cloak is displayed in the below.
Left figure, at at time step 90dt, shows the front of electric wave, Ex inside the AGLLH EM cloak R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 propagation
Right figure, at at time step 90dt, shows the front of electric wave, Ex inside the GLLH EM cloak R1 ≤ r ≤ R2 propagation

IX. HISTORY AND DISCUSSION
We discovered the GILD double layer clock phenomenon [ 1 ] to prevent detection by external EM waves in 2001. The double layer clock was appeared in the residual magnetic field Hy during GILD EM modeling and inversion [ 1 ]. Repeated GILD simulations show that the GILD double-layer cloth cloak is a mathematical-physical phenomenon. In 2003, we developed a completely new GL EM modeling [ 2 ] and GL EM inversion [ 3 ] in 2003 to investigate this strange phenomenon. We found mirages[ 5 ] and double layer cloaks [ 9 – 13 ]. Our GLLH EM cloaks in this paper and previous papers are based on GL EM modeling, inversion, and search class from Chen Jingyun’s GOLDBACH proof clue [21]. We deeply investigated the relationship between field and material interactive scattering and non scattering, proposed the GLLH EM cloak inversion. Our GL methods do not require artificial boundary conditions to truncate the infinite domain. The GL method does not need to solve large matrix equations . The GL method combines analytical method and numerical method. It can perform approaches, enabling analytical, numerical, or mixed field simulation and material generation. Front branching is a completely novel propagation method. The attracting front has the benefit of detecting exterior field information in invisible cloaked concealment.
In Figure 21, at the 84th time step, the EM wave propagates in the GLLH EM cloak and slower than the light speed of light. In Figure 22, at the 84th time step, the EM wave propagates through the Pendry cloak, its front split to into two phases ; the leading phase exceeds the speed of light. At the 90th time step , Figure 24 shows that the speed of the EM wave inside the Pendrycloak greatly exceeds the light speed of light . At the 90th time step, Figure 23 presents EM propagation in the GLLH EM cloak is presented in Figure 23; it is obvious that showing that the speed of the EM wave inside the GLLH EM cloak does not exceed the speed of light.
To overcome the infinite speed in [ 14 ], Ulf Leonhardt et al. proposed a new cloak with finite speed based ,on a Euclidean and non – Euclidean joint transform [ 17 ]. The ULF cloak overcomes the ” infinite speed ” physical violation, even though its refractive index is less than one in some sub domains , for example, n (σ, σ’, τ) = n ( 0. 75 π, π, τ) < 1. Our GLLH EM cloak without exceeding the speed of light and without time delay.
Theoretical analysis of GL EM modeling and inversion , along with numerous GLLH EM modeling simulations, verified that the GLLH EM cloak has full invisibility functions. The GLLH EM invisible cloaks avoid the two violations of infinite speed and superluminal propagation, and avoid the time delay. The novel EM wave propagations are presented in Figures 1 – 2 and 5 – 18.
The front inside the GLLH EM cloak curves completely around the concealment, forming a crescent – like shape in Figures 1 and 13. The two front teeth of the crescent front intersect at the branching point in Figures 14, 19, and 20. The branching points form a 2D subsurface. The wave front splits into two fronts at the front branching point. The outgoing front propagates forward and recovers to original wave front in free space. The attractive front propagates and shrinks to the inner boundary of the cloak, with its amplitude and speed rapidly decaying to zero. Using the GLLH EM cloak as the outer layer, the GLLH EM double cloak provides normal environment concealment. In its concealment, the EM wave field excited by the internal source propagates into the inner layer cloak, where its amplitude and speed rapidly decay to zero before the outer boundary of the inner layer cloak. Therefore, the GLLH EM double invisible cloak overcomes the three physical violations in other cloaks.
The GLLH EM double invisible cloak can be practical. GLLH EM cloak software can generate various scale full invisible cloaks without exceeding light speed, and can generate GLLH EM double cloaks of various scales that have no physical violations and have wide applications.
The GLLH EM cloak, GLLH EM cloak modeling and inversion, and GLLH EM cloak software are patented and copyrighted by authors in GL Geophysical Laboratory.
The GL modeling and inversion method is an effective physical simulation method. It has dual abilities of the theoretical analysis and numerical simulations to study the cloak metamaterials, wide materials, and field scattering in physical sciences.
From the GLLH invisible cloak, we discovered positive space and negative space and invisible science; isotropic electromagnetic invisible GLHUA sphere; anisotropic electromagnetic invisible GLHUA cloak. What is the positive space and negative space? Just as before, without imaginary number, i=√(-1) , we cannot solve the equation x²+1=0 in the real number domain. Let’s ask: In polar coordinates on a two-dimensional plane, where ,(ρ,θ), ρ>0 , is a point on the plane, where is (-ρ,θ) for the same value θ? This question can intrigue students from elementary middle school to university, and has also attracted the attention of professors and scientists at all levels. In this article, we introduce the concepts of positive space and negative space. In the three-dimensional spherical coordinate system, the set of points with positive radial coordinates,(r,θ,φ), 0≤r≤+∞, is called three-dimensional positive space. This is the three-dimensional space we live in. In the three-dimensional spherical coordinate system, a point with negative radial coordinates,(-r,θ,φ) ,-∞≤-r≤-0 , is defined as three-dimensional negative space, as described in our paper [15][16]. The origin of the positive space can be anywhere. The point in the positive space,(r,θ,φ) , and the point in the negative space,(-r,θ,φ) , are corresponding points with the same longitude and latitude. The origin of the positive space, +0, and the origin of the negative space, -0, are corresponding points, but different points. The three-dimensional negative space is the corresponding space of the three-dimensional positive space. When we are awake, we act in all kinds of strange ways in the positive space; when we are asleep, our sweet dreams are in the negative space[26].
GLLH EM invisible cloak with novel two front branching, absorbing and creating wave front, without infinite speed and without superluminal and without time delay. GLLH EM invisible cloak is completely invisibility cloak first in the would. The preprint of this paper has been announced in arXiv.org/abs/1005.3999 on May 24, 2010. This version is just proofread in English.








GLLH Completely Invisible Cloak announced in arXiv.org/abs/1005.3999 on 2010-May-21 first of world without superluminal and without time delay and with relative refractive index > 1


At footnote on page 2 of ULf paper arXiv.org/abs/1105.0164v3, Ulf wrote that “The preprint [35] proposes a different method for cloaking without superluminal propagation.” Preprint [35] is arXiv.org/abs/1005.3999 by Xie & Jianhua Li et al.

Reference [35][ of ULF cloak paper arXiv.org/abs/1005.0164v3 is GLLH cloak paper arXiv.org/abs/1005.3999 by Gan. Xie, J.Li, Lee xie and Feng Xie.
Comments
Comments settings

LikeCommentShare
Add a comment…
Open Emoji Keyboard
No comments, yet.
Be the first to comment.Start the conversation

Professor in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Professor In Dayuling Super Science Center
LikeCommentShare